Conditional evaluation
Like variables, conditional evaluation is one of the key concepts you'll come across in programming. It is used to execute a certain action based on matched conditions.
Bash gives you four conditional keywords if, elif, else and fi.
-
Conditional evaluations must start with an
ifand end with anfi -
Conditional evaluations can contain zero or more
elif -
The base case or the fallback should be handled by in an
elsestatement
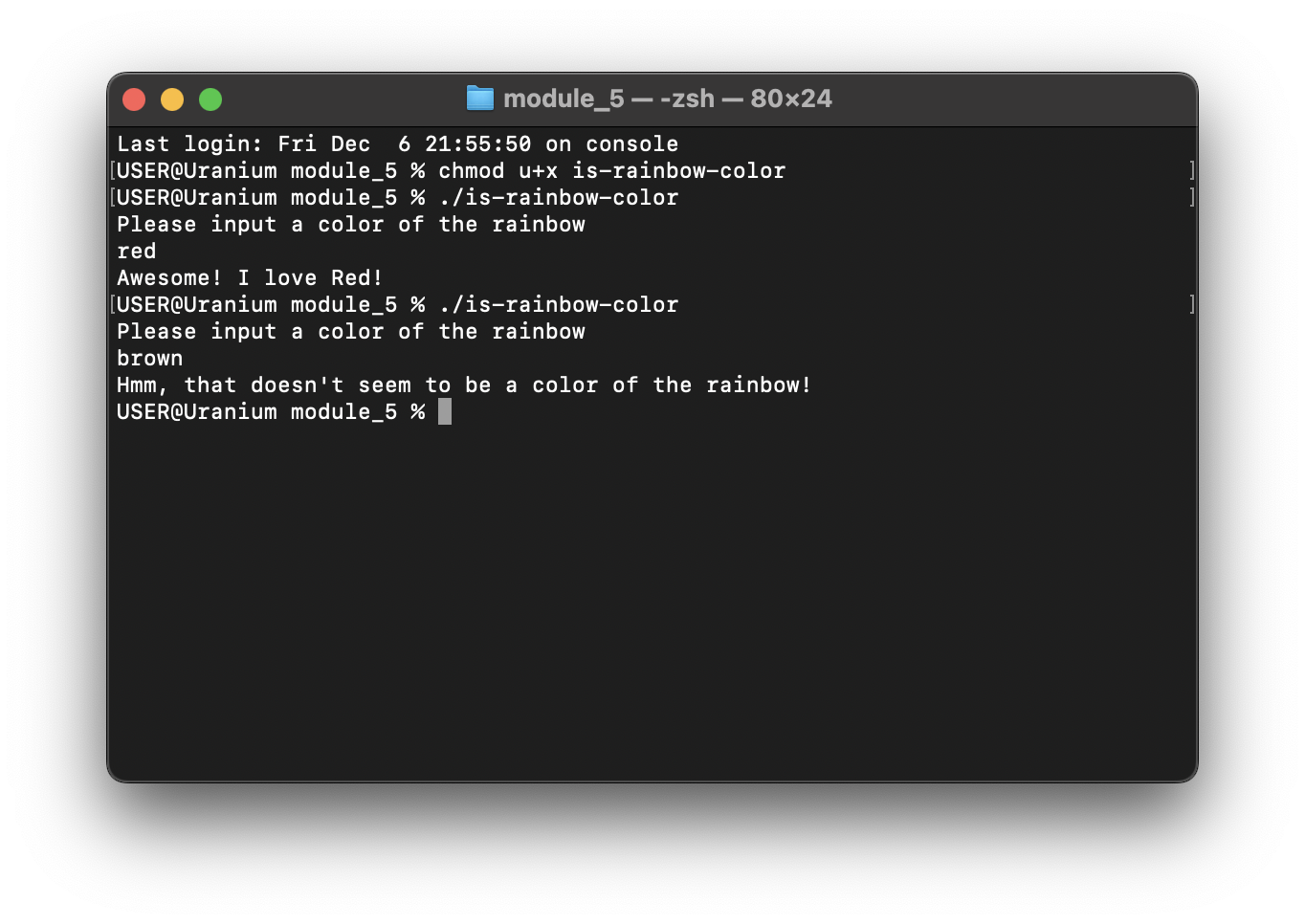
Consider the following example, we will read the input from the user and check if it is a rainbow color.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Please input a color of the rainbow"
read color
if [ "$color" = "red" ]; then
echo "Awesome! I love Red!"
elif [ "$color" = "orange" ]; then
echo "Bright and cheerful! Orange is great!"
elif [ "$color" = "yellow" ]; then
echo "Sunny! Yellow is wonderful!"
elif [ "$color" = "green" ]; then
echo "So fresh! Green is amazing!"
elif [ "$color" = "blue" ]; then
echo "Cool choice! Blue is calming!"
elif [ "$color" = "indigo" ]; then
echo "Unique and deep! Indigo is awesome!"
elif [ "$color" = "violet" ]; then
echo "Elegant! Violet is beautiful!"
else
echo "Hmm, that doesn't seem to be a color of the rainbow!"
fi
Consider Another example
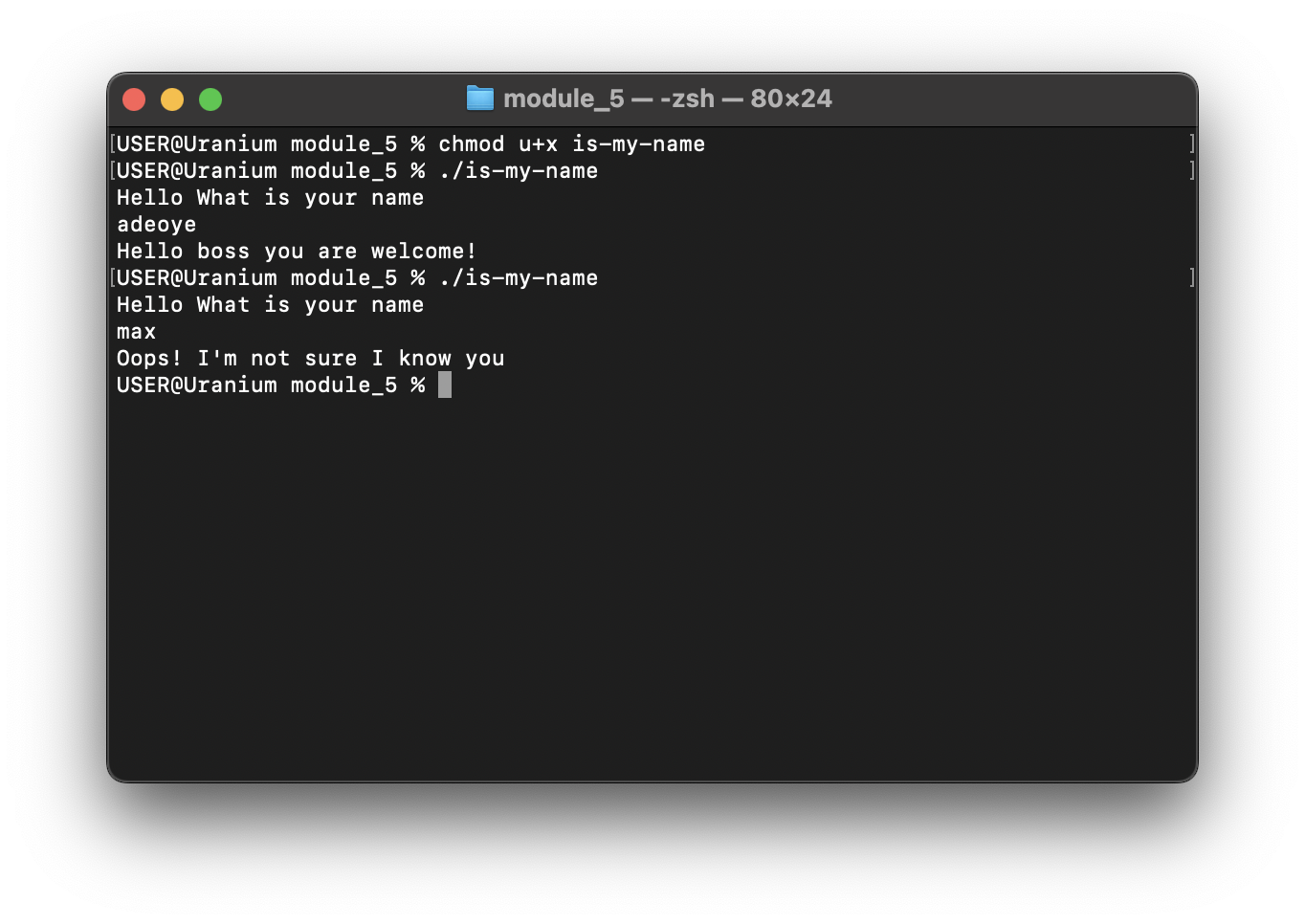
If my name is "adeoye", print "Hello boss you are welcome!", if not, print "oops! I'm not sure I know you"
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello What is your name"
read name
if [ $name = 'adeoye' ]; then
echo "Hello boss you are welcome!"
else
echo "Oops! I'm not sure I know you"
fi